AndroidNativeEmu和unidbg都是对unicorn进行了一定程度封装的开源项目,让我们可以很方便的调用jni函数,以及对没有实现的函数进行hook实现处理。并且让我们可以实现so里面模拟调用java函数。下面首先使用AndroidNativeEmu来对抗ollvm的字符串混淆。对so进行修复。让我们可以更加便捷的进行静态分析。
在实现之前,先总结下原理。
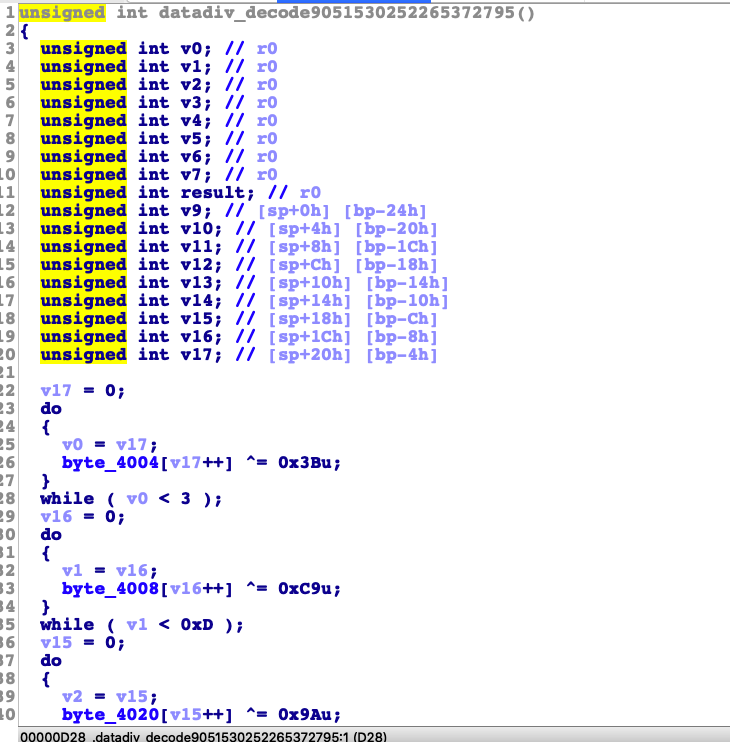
ollvm的字符串混淆,我们使用ida的时候。看到的结果如下。
这里相当于是一个解密函数。通过这个函数将会还原成正常的字符串。然后我们看看在哪里调用到了这个解密函数
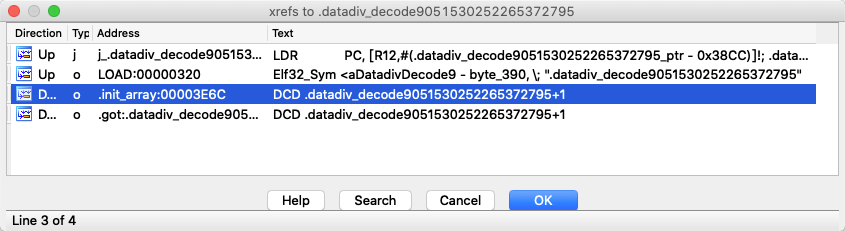
可以看到是在.init_array中使用解密函数对字符串进行还原。也就是说。当我们执行完.init_array后。就会将正常的字符串写入内存中。这时我们就得到了真正的字符串了。所以根据这个情况。
第一步,我们需要监控内存的读写,然后运行.init_array。这样发生的内存写入时,基本可以确定是字符串还原函数在写入恢复的字符串。
写之前我们先看看unicorn的内存写入的相关注释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 /* Callback function for hooking memory (READ, WRITE & FETCH) @type: this memory is being READ, or WRITE @address: address where the code is being executed @size: size of data being read or written @value: value of data being written to memory, or irrelevant if type = READ. @user_data: user data passed to tracing APIs */
这里就知道了。size是写入或读取数据的长度,value是写入或读取的数据。那么开始写我们第一步的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import loggingimport sysfrom unicorn import UC_HOOK_MEM_WRITEimport structfrom androidemu.emulator import Emulatorlogging.basicConfig( stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.DEBUG, format="%(asctime)s %(levelname)7s %(name)34s | %(message)s" ) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) def hook_mem_write (uc,type,address,size,value,userdata ): curdata=struct.pack("I" ,value)[:size] print(curdata) emulator = Emulator(vfp_inst_set=True ) emulator.load_library("example_binaries/libc.so" , do_init=False ) emulator.mu.hook_add(UC_HOOK_MEM_WRITE, hook_mem_write) lib_module = emulator.load_library("example_binaries/obf.so" , do_init=True )
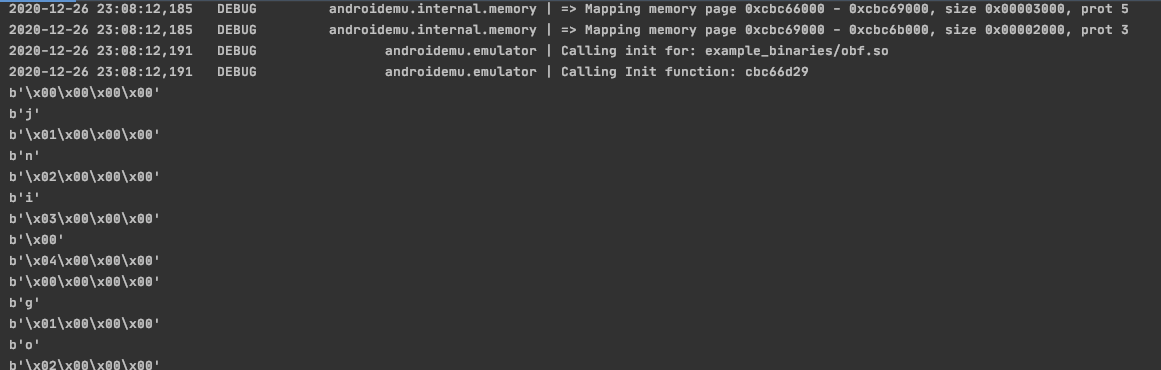
输出的结果如下
这里能看到。真实的字符串已经能在回调监控中打印出来了。接下来的第二步,我们需要把所有真实字符串以及写入真实字符串的位置给保存下来。
1 2 3 4 5 dstr_datas={} def hook_mem_write (uc,type,address,size,value,userdata ): curdata=struct.pack("I" ,value)[:size] dstr_datas[address]=curdata print(curdata)
这样我们就将init_array过程中所有还原出来的真实字符串给保存下来了。最后我们要将我们的真实字符串再写回so中。那么写回到哪里呢?我们监控内存写入时,当时是给什么地址写入数据。我们就写入到哪里。这样我们写入的so就能直接在ida中打开就看到真实字符串了。在写入时需要注意的是。我们保存的address是有一个基址的。也就是说。我们写入时需要减掉基址。才是真正应该写入的位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 base_addr=lib_module.base sofile=open("example_binaries/obf.so" ,"rb" ) sodata=sofile.read() for address,v in dstr_datas.items(): if address > base_addr and address < base_addr+lib_module.size: offset=address-base_addr print("address:0x%x data:%s offset:0x%x" % (address, v,offset))
然后我贴上几行打印的内容
1 2 3 4 5 address:0xcbc6a004 data:b'j' offset:0x4004 address:0xcbc6a005 data:b'n' offset:0x4005 address:0xcbc6a006 data:b'i' offset:0x4006 address:0xcbc6a007 data:b'\x00' offset:0x4007 address:0xcbc6a008 data:b'g' offset:0x4008
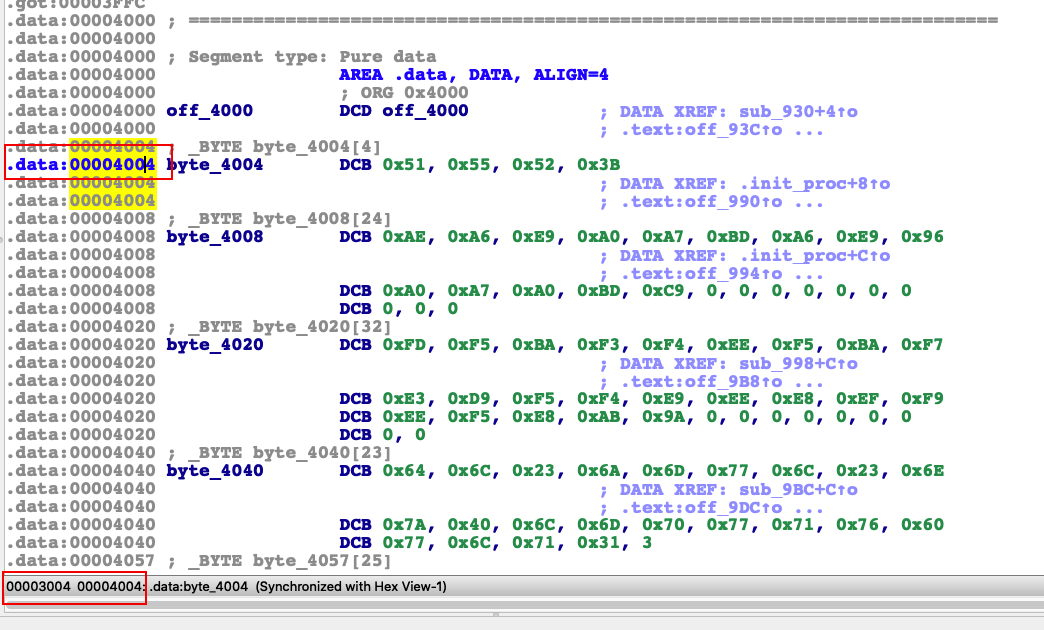
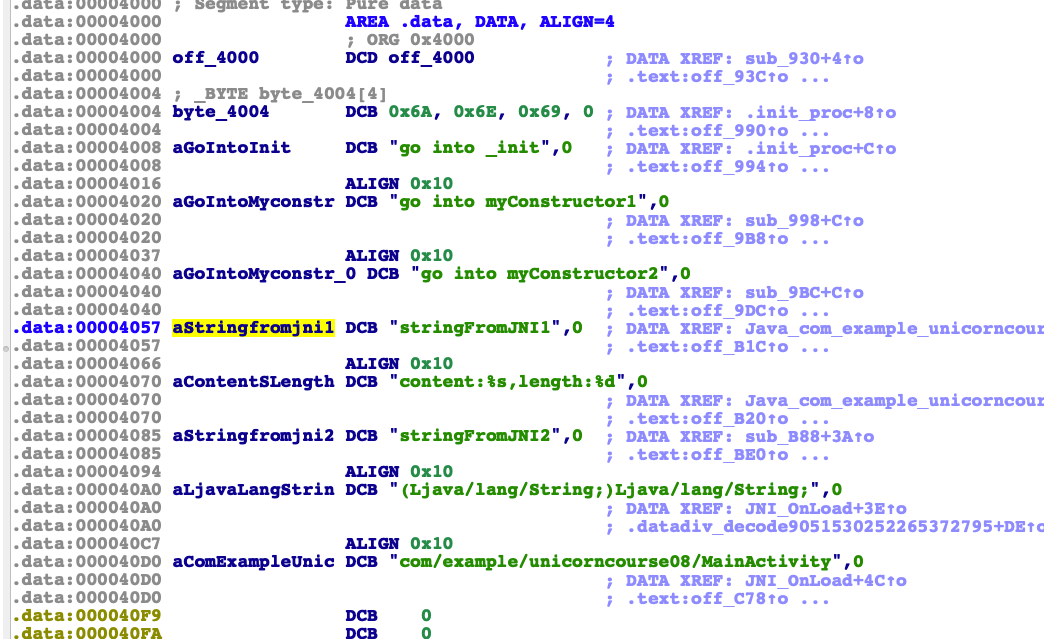
第一个offset的偏移是0x4004。那么我们打开ida检查一下。是否对的上
能看到ida里面显示的确实是对的上的。但是这里要留意最左下角的00003004。实际这个才是文件中的真实位置。所以我们这里直接写回so要再将offset-0x1000。下面我们开始将so的数据修改。并且保存成一个新的文件。最后贴上完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import loggingimport sysfrom unicorn import UC_HOOK_MEM_WRITEimport structfrom androidemu.emulator import Emulatorlogging.basicConfig( stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.DEBUG, format="%(asctime)s %(levelname)7s %(name)34s | %(message)s" ) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) dstr_datas={} def hook_mem_write (uc,type,address,size,value,userdata ): curdata=struct.pack("I" ,value)[:size] dstr_datas[address]=curdata emulator = Emulator(vfp_inst_set=True ) emulator.load_library("example_binaries/libc.so" , do_init=False ) emulator.mu.hook_add(UC_HOOK_MEM_WRITE, hook_mem_write) modulePath="example_binaries/obf.so" lib_module = emulator.load_library(modulePath, do_init=True ) base_addr=lib_module.base sofile=open("example_binaries/obf.so" ,"rb" ) sodata=sofile.read() sofile.close() for address,v in dstr_datas.items(): if address > base_addr and address < base_addr+lib_module.size: offset=address-base_addr-0x1000 print("address:0x%x data:%s offset:0x%x" % (address, v,offset)) sodata=sodata[:offset]+v+sodata[offset+len(v):] savepath=modulePath+".new" nfile=open(savepath,"wb" ) nfile.write(sodata) nfile.close()
那么实际效果怎么样呢。我们打开ida来对比一下修改前和修改后的效果
修改前
修改后
接着再使用unidbg来实现一次字符串的反混淆
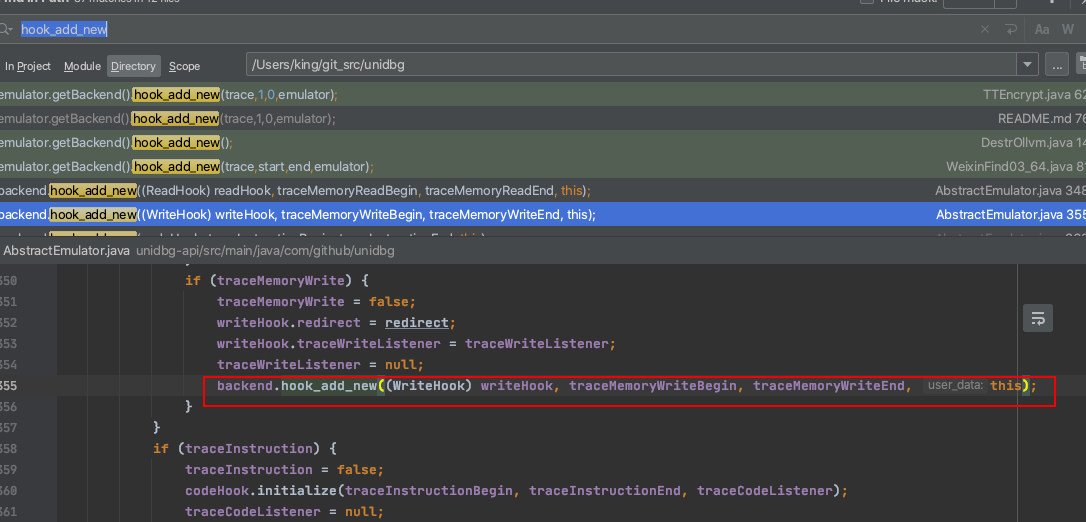
按照上面的思路。我们首先设置内存写入的监控,然后加载so。而unidbg在加载的时候。就会自动的执行init和init_array。所以我们接下来看看unidbg是怎么进行内存的写入监控的。搜索一下unidbg源码。就能找到是如何使用的了。我们搜索hook_add_new
这里我们就知道了是设置了一个TraceMemoryHook对象进行监控的。由于我们是需要自己修改里面监控后的逻辑。所以不要变动他原有的。拷贝一份出来。然后删除里面原有的打印逻辑。再加上我们之前逻辑。也就是打印一下写入的数据。将监控到的写入数据和写入地址给保存起来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class DeStrWriteHook implements WriteHook private final boolean read; DeStrWriteHook(boolean read) { this .read = read; } PrintStream redirect; TraceWriteListener traceWriteListener; public Map<Long,byte []> dstr_datas=new HashMap<Long,byte []>(); public static byte [] longToBytesBig(long n) { byte [] b = new byte [8 ]; b[7 ] = (byte ) (n & 0xff ); b[6 ] = (byte ) (n >> 8 & 0xff ); b[5 ] = (byte ) (n >> 16 & 0xff ); b[4 ] = (byte ) (n >> 24 & 0xff ); b[3 ] = (byte ) (n >> 32 & 0xff ); b[2 ] = (byte ) (n >> 40 & 0xff ); b[1 ] = (byte ) (n >> 48 & 0xff ); b[0 ] = (byte ) (n >> 56 & 0xff ); return b; } public static byte [] longToBytesLittle(long n) { byte [] b = new byte [8 ]; b[0 ] = (byte ) (n & 0xff ); b[1 ] = (byte ) (n >> 8 & 0xff ); b[2 ] = (byte ) (n >> 16 & 0xff ); b[3 ] = (byte ) (n >> 24 & 0xff ); b[4 ] = (byte ) (n >> 32 & 0xff ); b[5 ] = (byte ) (n >> 40 & 0xff ); b[6 ] = (byte ) (n >> 48 & 0xff ); b[7 ] = (byte ) (n >> 56 & 0xff ); return b; } @Override public void hook (Backend backend, long address, int size, long value, Object user) if (read) { return ; } try { Emulator<?> emulator = (Emulator<?>) user; if (traceWriteListener == null || traceWriteListener.onWrite(emulator, address, size, value)) { byte [] writedata=longToBytesLittle(value); byte [] resizeWriteData=new byte [size]; System.arraycopy(writedata,0 ,resizeWriteData,0 ,size); dstr_datas.put(address,resizeWriteData); } } catch (BackendException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e); } } }
然后我们按之前的步骤。使用这个类来hook。并且遍历一下我们保存出来的结果看和AndroidNativeEmu是不是一致的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public class DestrOllvm private final AndroidEmulator emulator; public DeStrWriteHook trace; public Module module ; public DestrOllvm () emulator=new AndroidARMEmulator("com.example.unicorncourse08" ); try { trace = new DeStrWriteHook(false ); final Memory memory=emulator.getMemory(); LibraryResolver resolver = new AndroidResolver(23 ); memory.setLibraryResolver(resolver); emulator.getBackend().hook_add_new(trace,1 ,0 ,emulator); module =emulator.loadLibrary(new File("unidbg-android/src/test/resources/example_binaries/obf.so" )); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static byte [] readFile(String strFile){ try { InputStream is = new FileInputStream(strFile); int iAvail = is.available(); byte [] bytes = new byte [iAvail]; is.read(bytes); is.close(); return bytes; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return null ; } public static void main (String[] args) DestrOllvm destr=new DestrOllvm(); String savepath="unidbg-android/src/test/resources/example_binaries/obf.so.new" ; byte [] sodata=readFile("unidbg-android/src/test/resources/example_binaries/obf.so" ); long base_addr=destr.module .base; long module_size=destr.module .size; for (Map.Entry<Long, byte []> item : destr.trace.dstr_datas.entrySet()){ if (item.getKey()>base_addr && item.getKey()<base_addr+module_size){ long offset=item.getKey()-base_addr-0x1000 ; System.out.println(String.format("address:0x%x data:%s" ,offset, OtherTools.byteToString(item.getValue()))); } } } }
然后看看打印的结果和之前是不是差不多的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 address:0x3004 data:6A address:0x3005 data:6E address:0x3006 data:69 address:0x3007 data:00 address:0x3008 data:67 address:0x3009 data:6F address:0x300a data:20 address:0x300b data:69 address:0x300c data:6E
对比AndroidNativeEmu的日志是正确的。那么我们完成最后的步骤。生成新的so文件,下面贴上完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 public class DestrOllvm private final AndroidEmulator emulator; public DeStrWriteHook trace; public Module module ; public DestrOllvm () emulator=new AndroidARMEmulator("com.example.unicorncourse08" ); try { trace = new DeStrWriteHook(false ); final Memory memory=emulator.getMemory(); LibraryResolver resolver = new AndroidResolver(23 ); memory.setLibraryResolver(resolver); emulator.getBackend().hook_add_new(trace,1 ,0 ,emulator); module =emulator.loadLibrary(new File("unidbg-android/src/test/resources/example_binaries/obf.so" )); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static byte [] readFile(String strFile){ try { InputStream is = new FileInputStream(strFile); int iAvail = is.available(); byte [] bytes = new byte [iAvail]; is.read(bytes); is.close(); return bytes; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return null ; } public static void writeFile (byte [] data,String savefile) try { FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(savefile); BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos); bos.write(data,0 ,data.length); bos.flush(); bos.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main (String[] args) DestrOllvm destr=new DestrOllvm(); String savepath="unidbg-android/src/test/resources/example_binaries/obf.so.new" ; byte [] sodata=readFile("unidbg-android/src/test/resources/example_binaries/obf.so" ); long base_addr=destr.module .base; long module_size=destr.module .size; ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); for (Map.Entry<Long, byte []> item : destr.trace.dstr_datas.entrySet()){ if (item.getKey()>base_addr && item.getKey()<base_addr+module_size){ baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); Long offset=item.getKey()-base_addr-0x1000 ; System.out.println(String.format("address:0x%x data:%s" ,offset, OtherTools.byteToString(item.getValue()))); byte [] start=new byte [offset.intValue()]; System.arraycopy(sodata,0 ,start,0 ,offset.intValue()); int endsize=sodata.length-offset.intValue()-item.getValue().length; byte [] end=new byte [endsize]; System.arraycopy(sodata,offset.intValue()+item.getValue().length,end,0 ,endsize); baos.write(start,0 ,start.length); baos.write(item.getValue(),0 ,item.getValue().length); baos.write(end,0 ,end.length); sodata=baos.toByteArray(); } } writeFile(baos.toByteArray(),savepath); } }
最后ida打开一下生成的so看看结果
最后我们将libcrypt.so以及libcrack.so都直接用unidbg跑一次。然后下面贴上ida查看这两个so的结果
Libcrypt.so的ida结果如下
Libcrack.so的ida结果如下